Telescope
What is a Galileo telescope?
Duration: 10
Place the lens cubes on the sheet as shown in the diagram, then peer through the telescope into the distance.
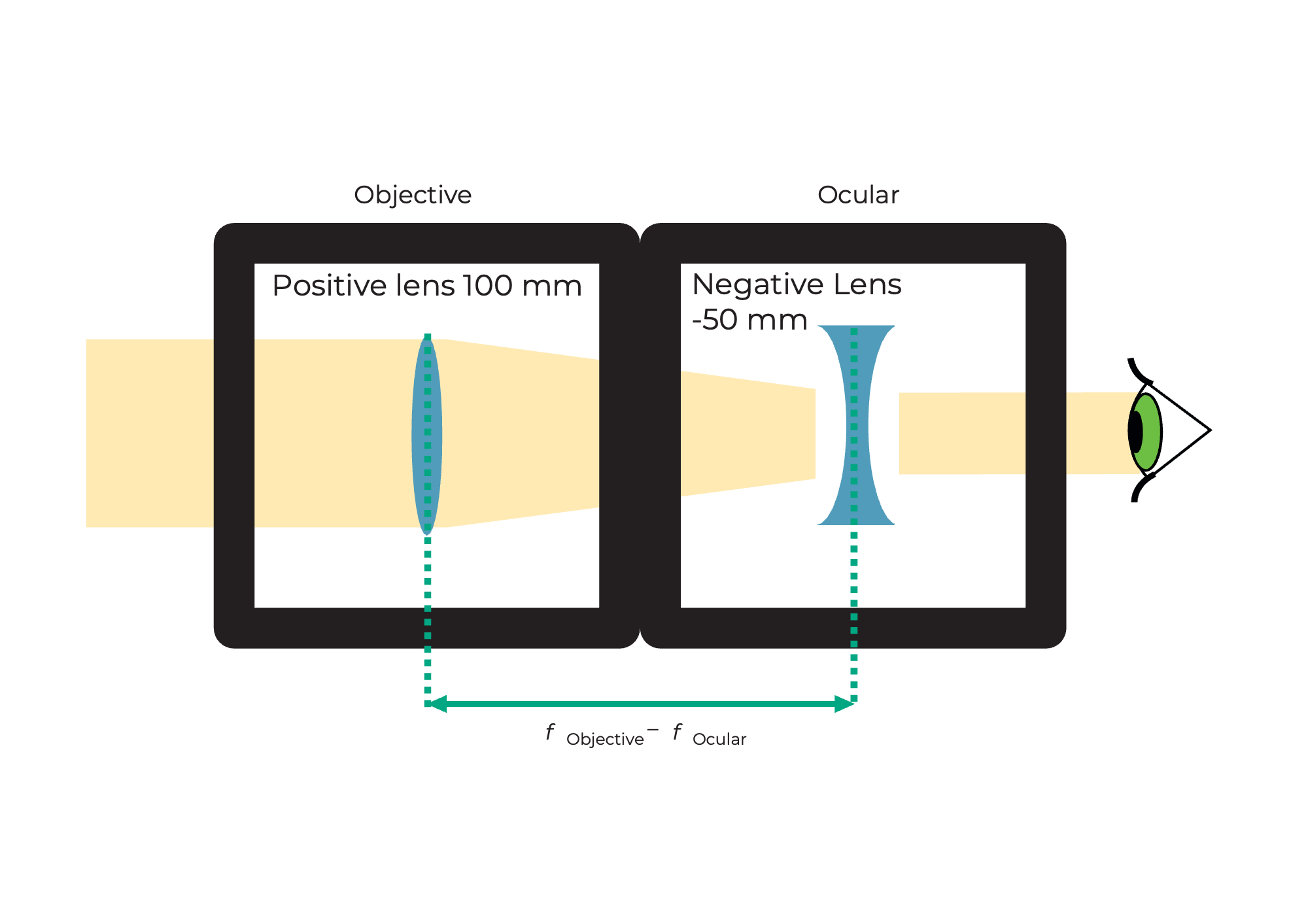
This is a Galileo telescope
A telescope is an optical instrument that makes distant objects appear many times closer or larger.
The lens on the object side is called the objective lens.
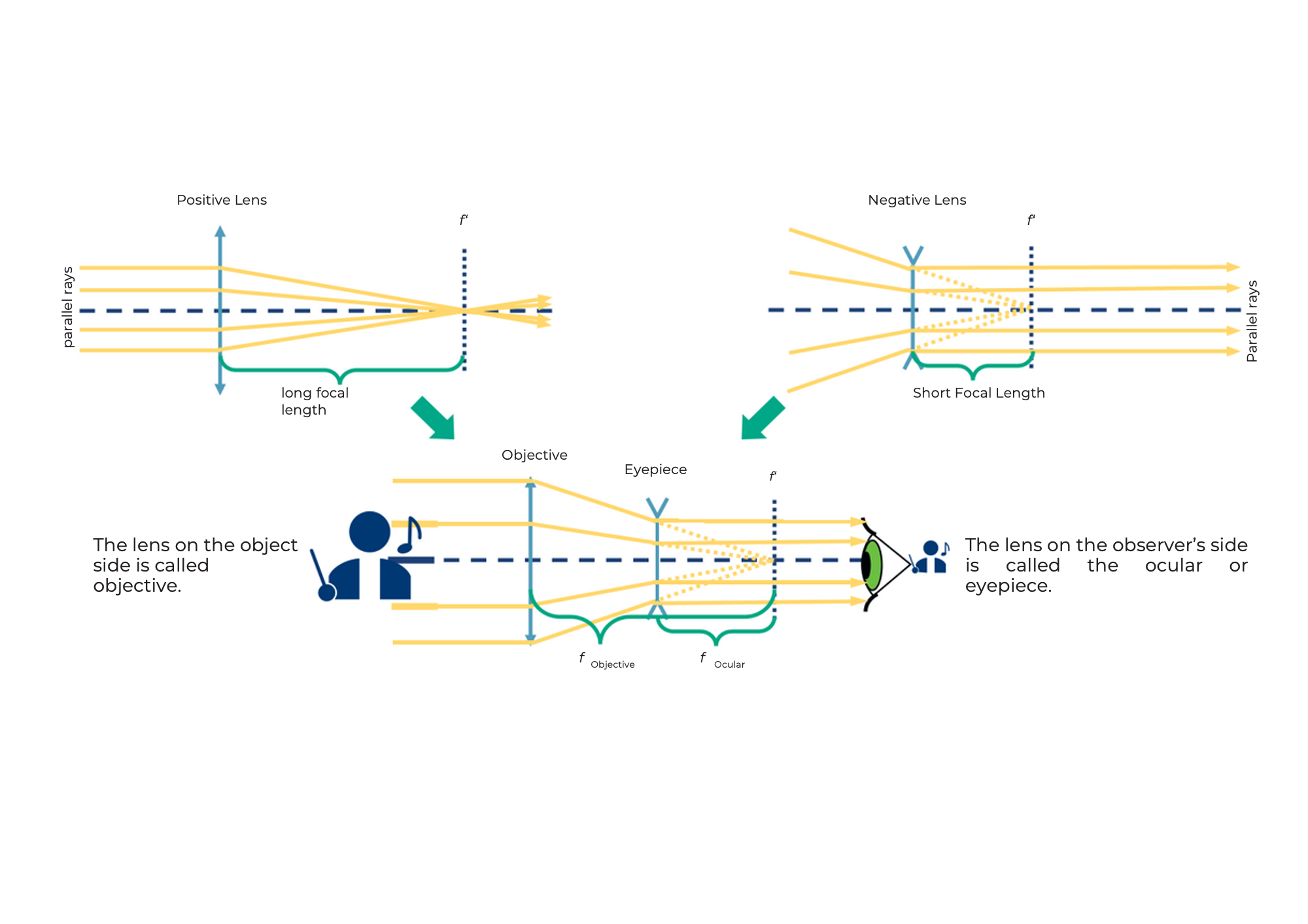
The lens facing the eye is called the eyepiece. The Galileo telescope is also used in opera glasses.
This is how the Galileo telescope works
What is the magnification of this Galileo telescope?

Formula for calculating magnification

It is not possible to achieve very high magnification with this telescope. But it is very compact.
- Magnified with the magnification from the formula above
- Upright
- Right reading
The field of view is small.
Tutorial: Galileo's telescope

Materials needed:
- Four base plates
- 100 mm positive lens (in cube)
- -50 mm negative lens (in cube)

Diagram (side view):
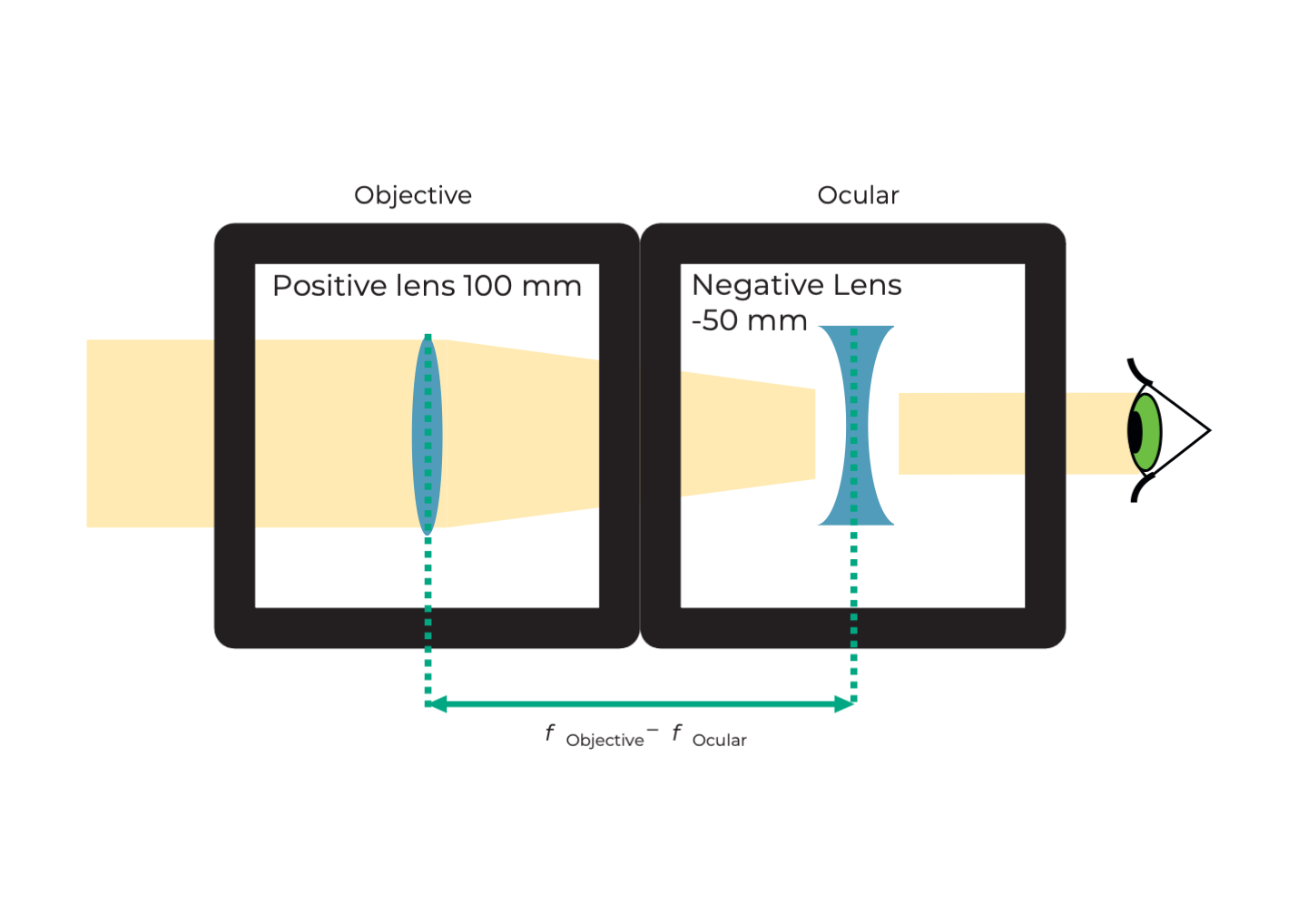
Instructions for assembling Galileo's telescope:
Step 1: Place the base plates on top
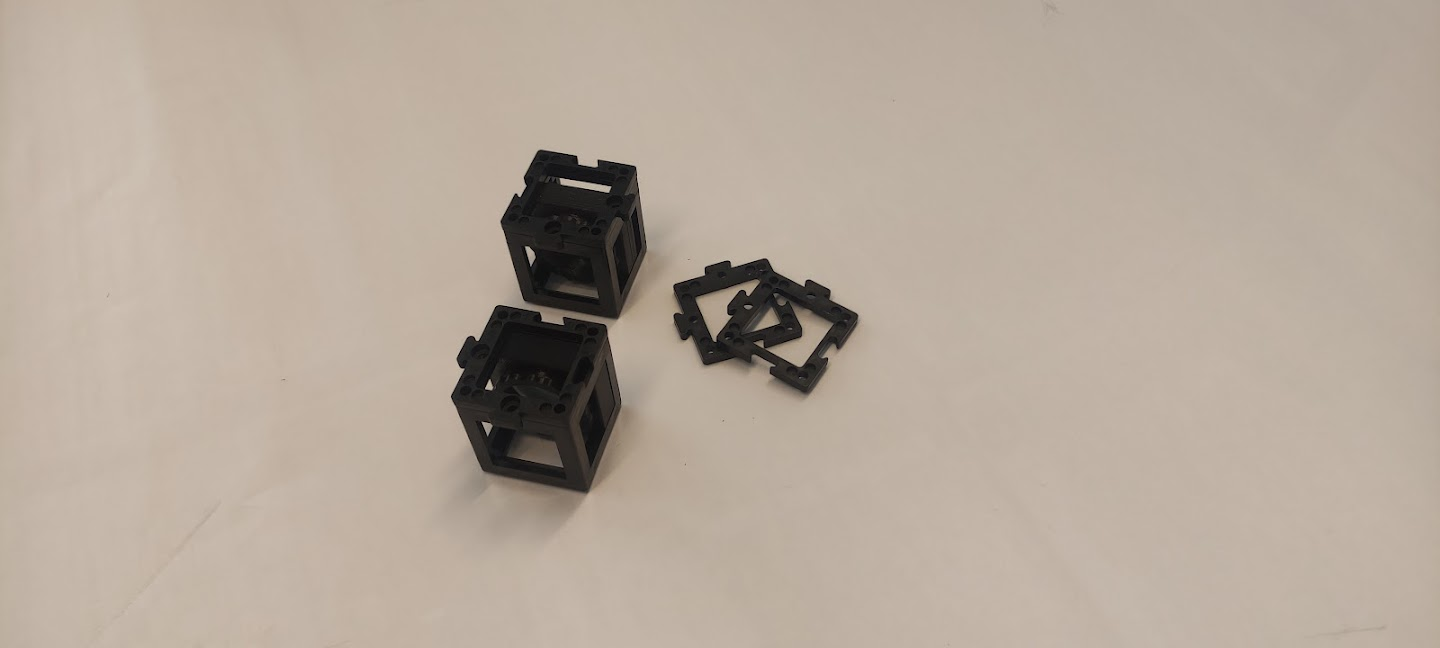 Place one base plate on top of each lens cube.
Place one base plate on top of each lens cube.
Step 2: Place the base plates on the bottom
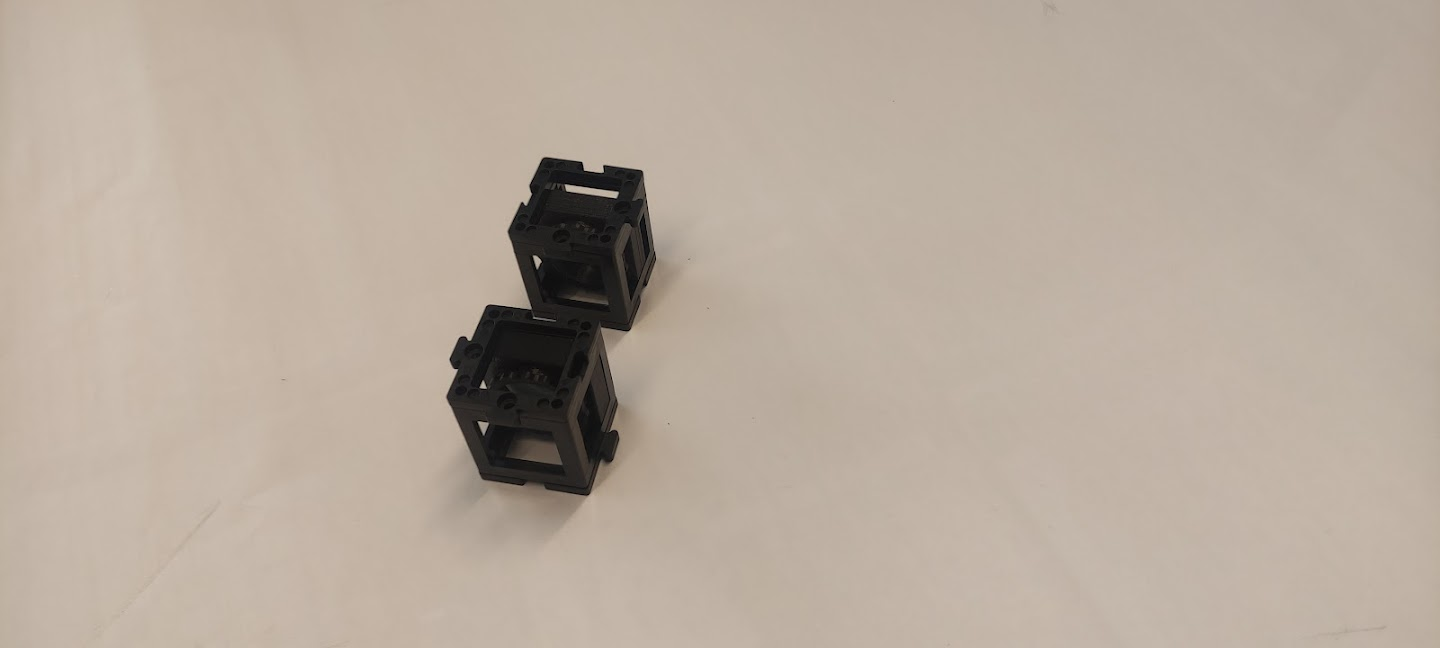 Place one base plate on the bottom of each lens cube.
Place one base plate on the bottom of each lens cube.
Step 3: Assemble the cubes
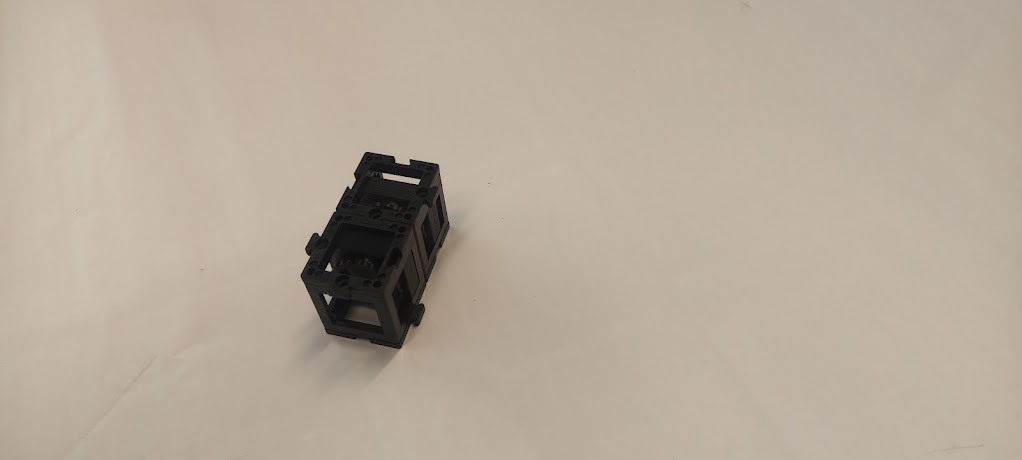 Assemble the two cubes in such a way that the distance between the lenses' surfaces is the longest.
Assemble the two cubes in such a way that the distance between the lenses' surfaces is the longest.
Step 4: Adjust the lenses' distance
 Adjust distance between negative and positive lens to the maximum possible.
Adjust distance between negative and positive lens to the maximum possible.
Step 5: Use the telescope!
 Search for an object to the distance and use Galileo's telescope to look at it.
Search for an object to the distance and use Galileo's telescope to look at it.
What is a Kepler telescope?
Set the lenses in the correct positions as shown in the diagram. Then look through the telescope into the distance.

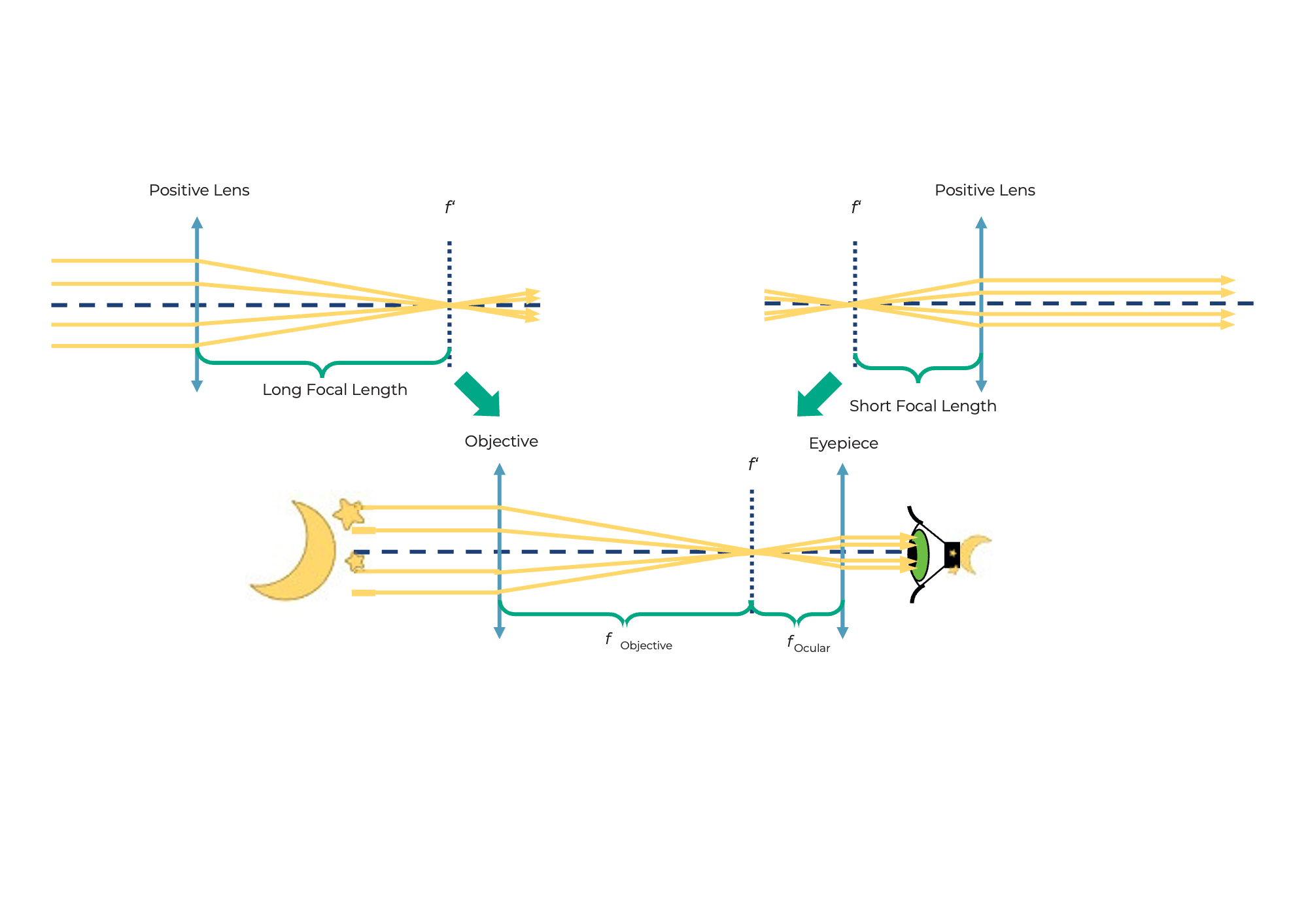
This is a Kepler telescope
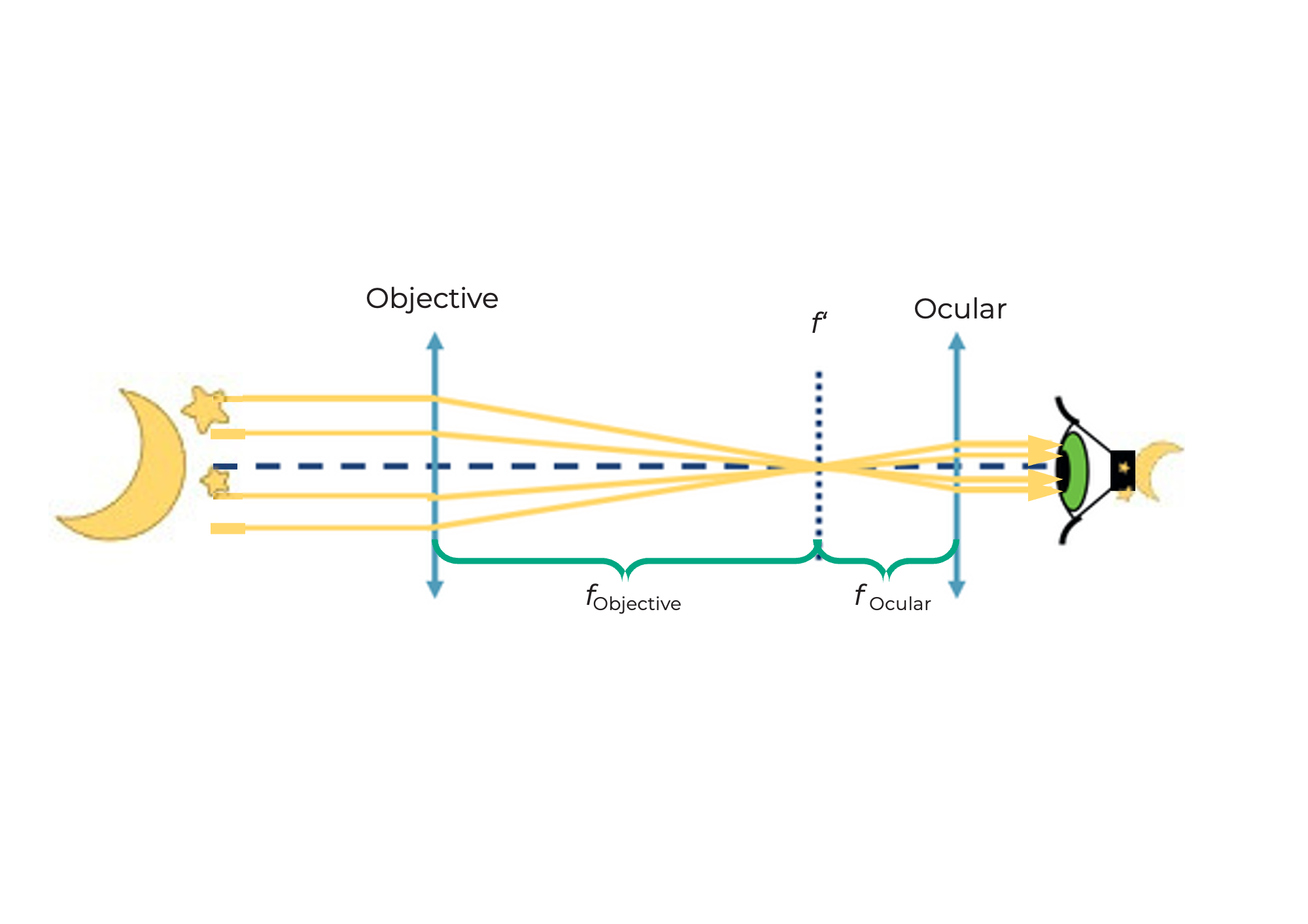
This type of telescope is often used in astronomy.
This is how the Kepler telescope works
What is the magnification of this Kepler telescope?

Formula for calculating magnification
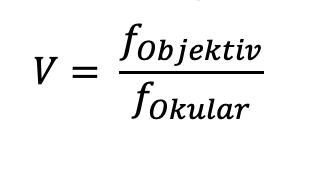
This telescope can achieve a higher magnification than the Galilean telescope. But it creates the opposite picture. However, this is not a problem for observing the stars.
- Magnified by the magnification from the formula above
- Vice versa
- Sides reversed
The field of view is larger than with the Galileo telescope.
Tutorial: Kepler's Telescope
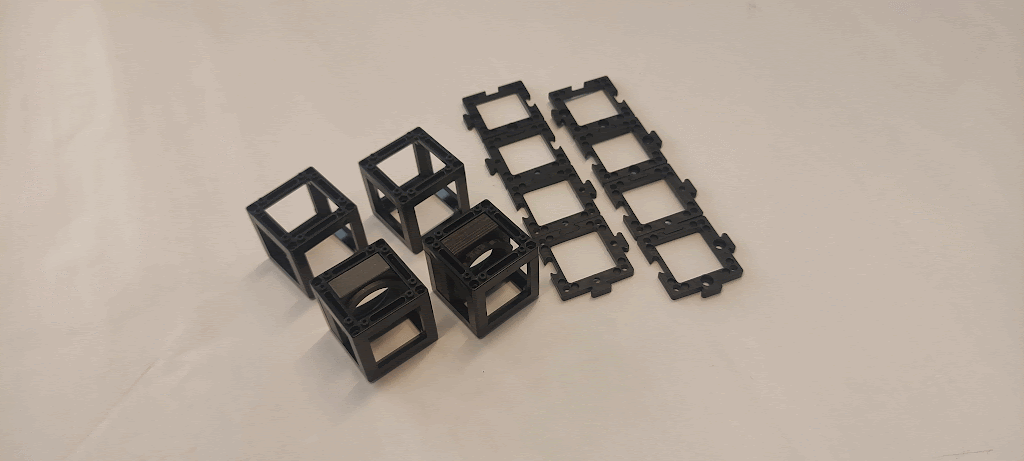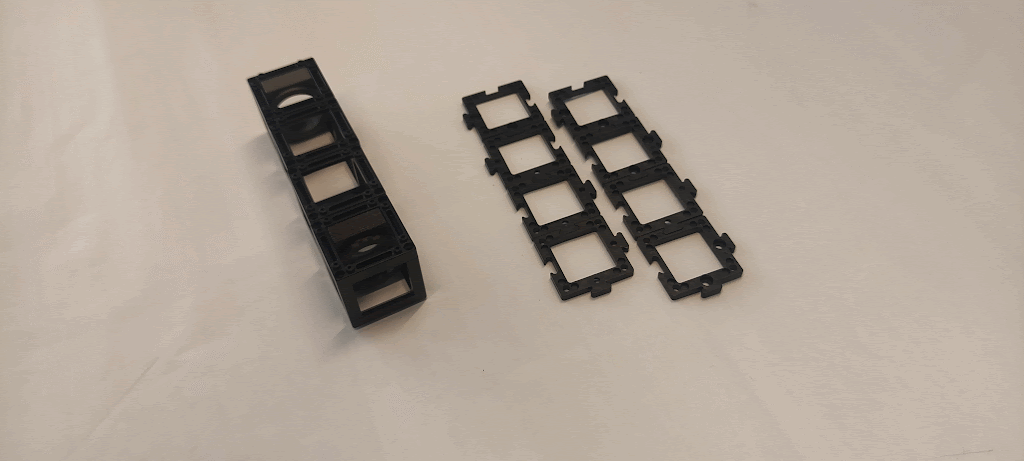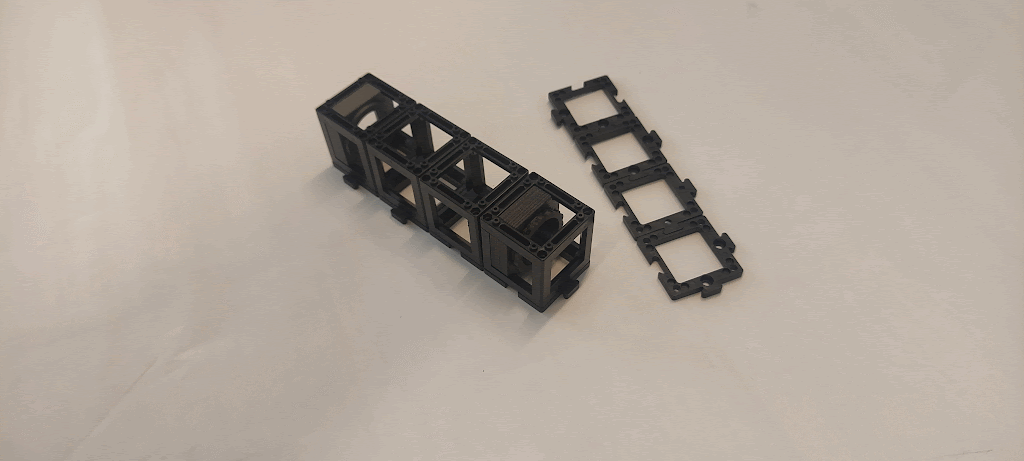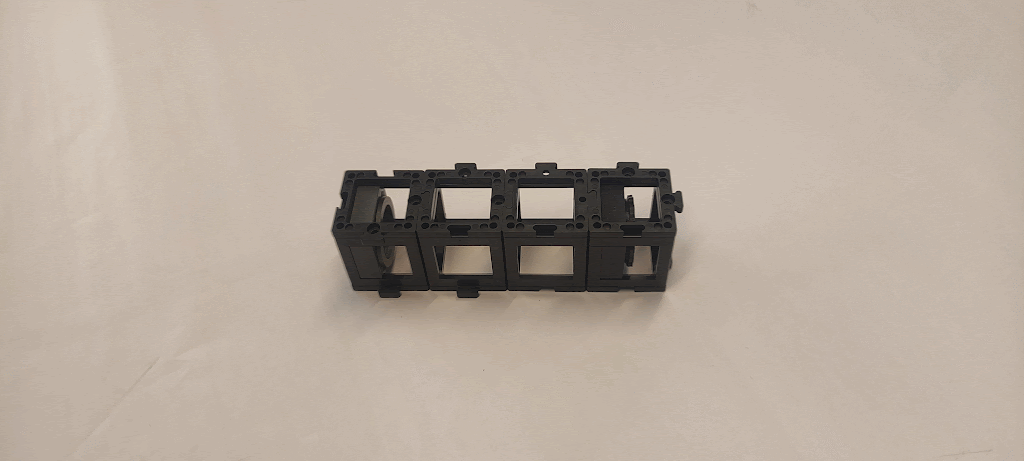
Materials needed:
- Eight base plates
- 100 mm positive lens (in cube)
- 50 mm positive lens (in cube)
- Two empty cubes

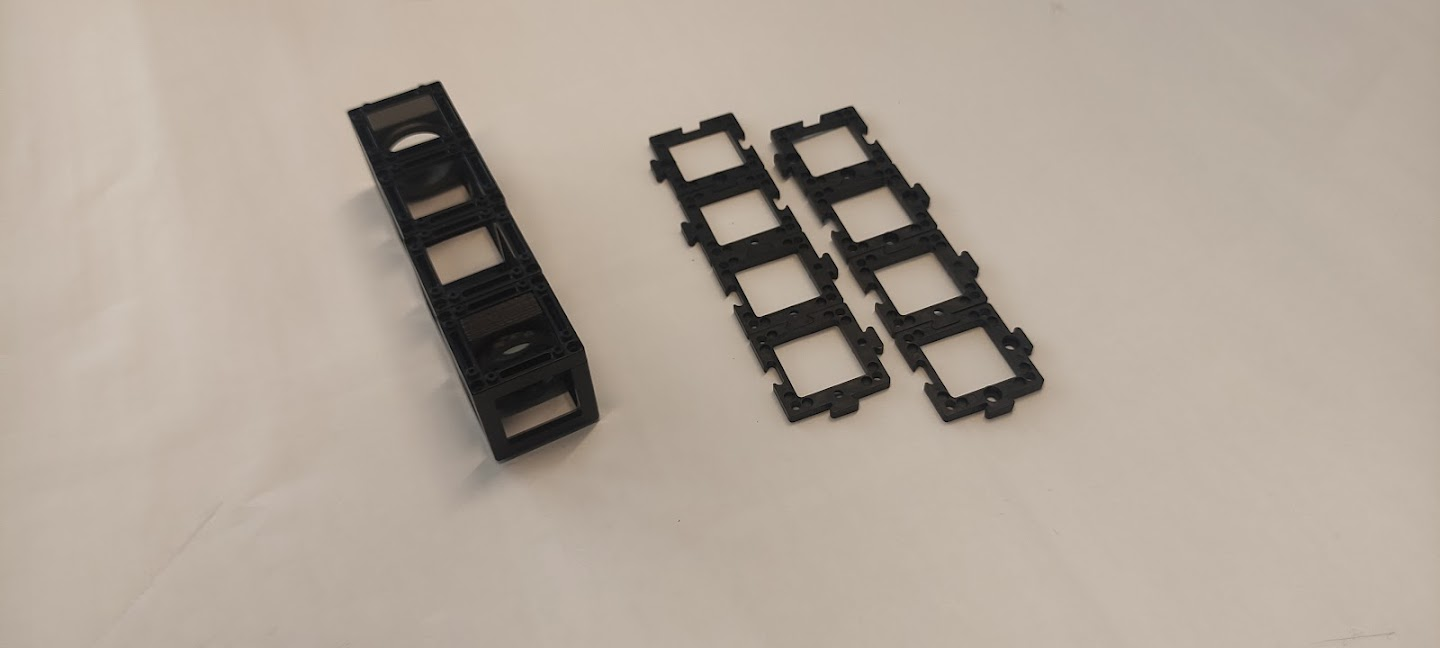
Diagram (side view):
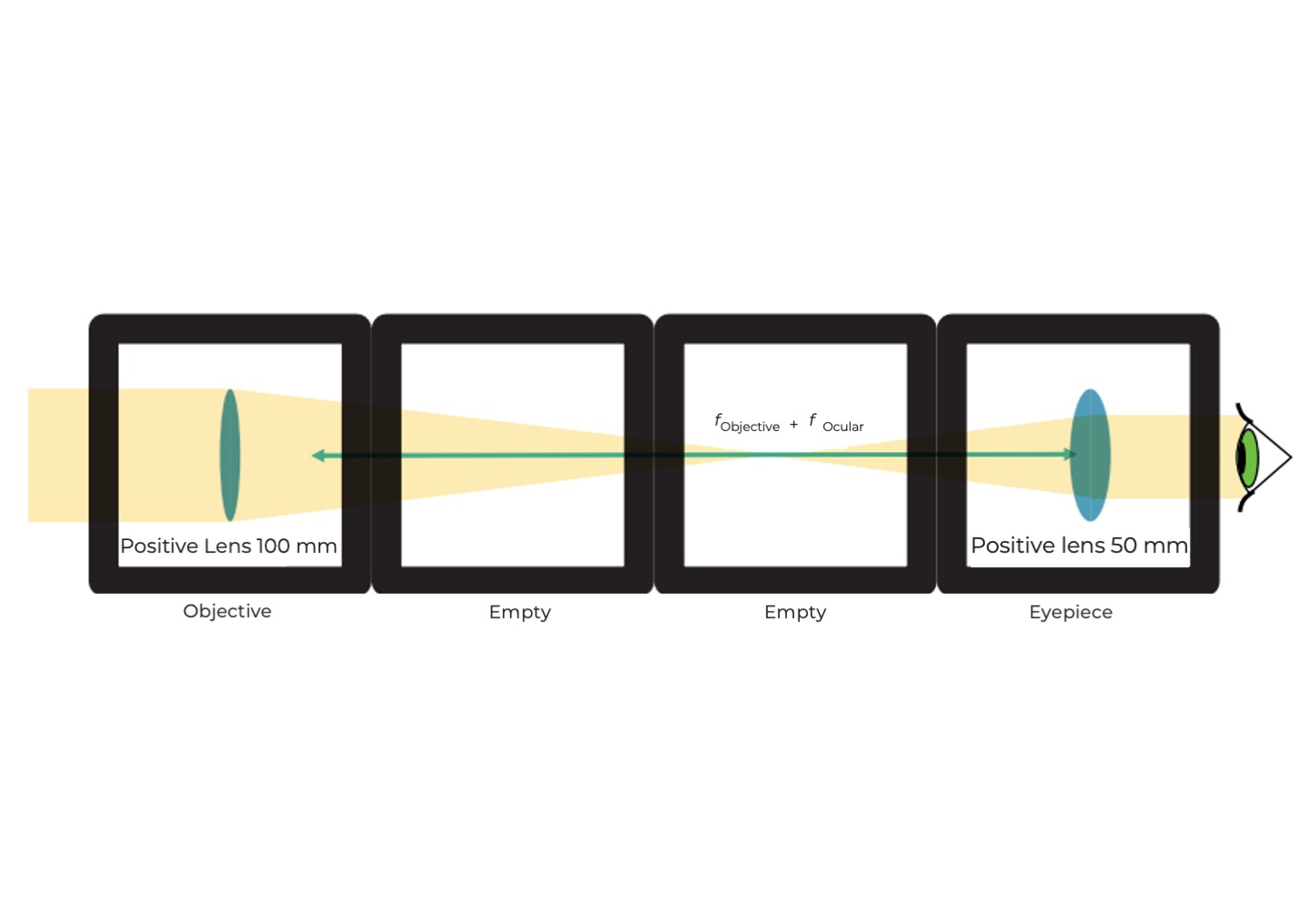
Instructions for assembling Kepler's telescope:
Step 1: Align the cubes
Align the cubes such that the two lenses lay at the extremes and the two empty cubes in the middle.

Step 2: Fix the cubes with base plates
Fix the cubes with the base plates placing them on top and on the bottom.

Step 3: Adjust the distance
Adjust the distance between the lenses as shown in the image.

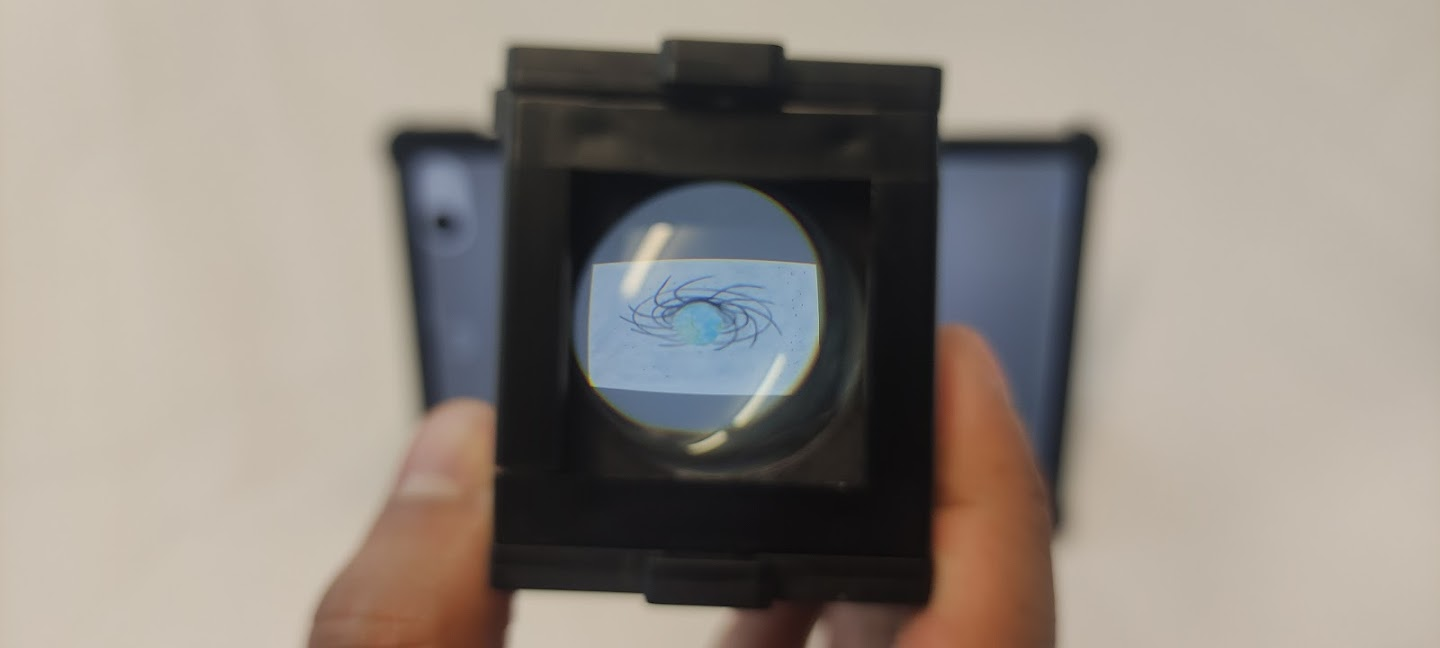
Step 4: Use Kepler's telescope
Look for an object to the distance and use Kepler's telescope to look at it.
What is a spotting scope?
The spotting scope is long, so the scheme is not the same size. Set the lenses in the correct positions as shown in the diagram and look into the distance through the telescope.

which results into
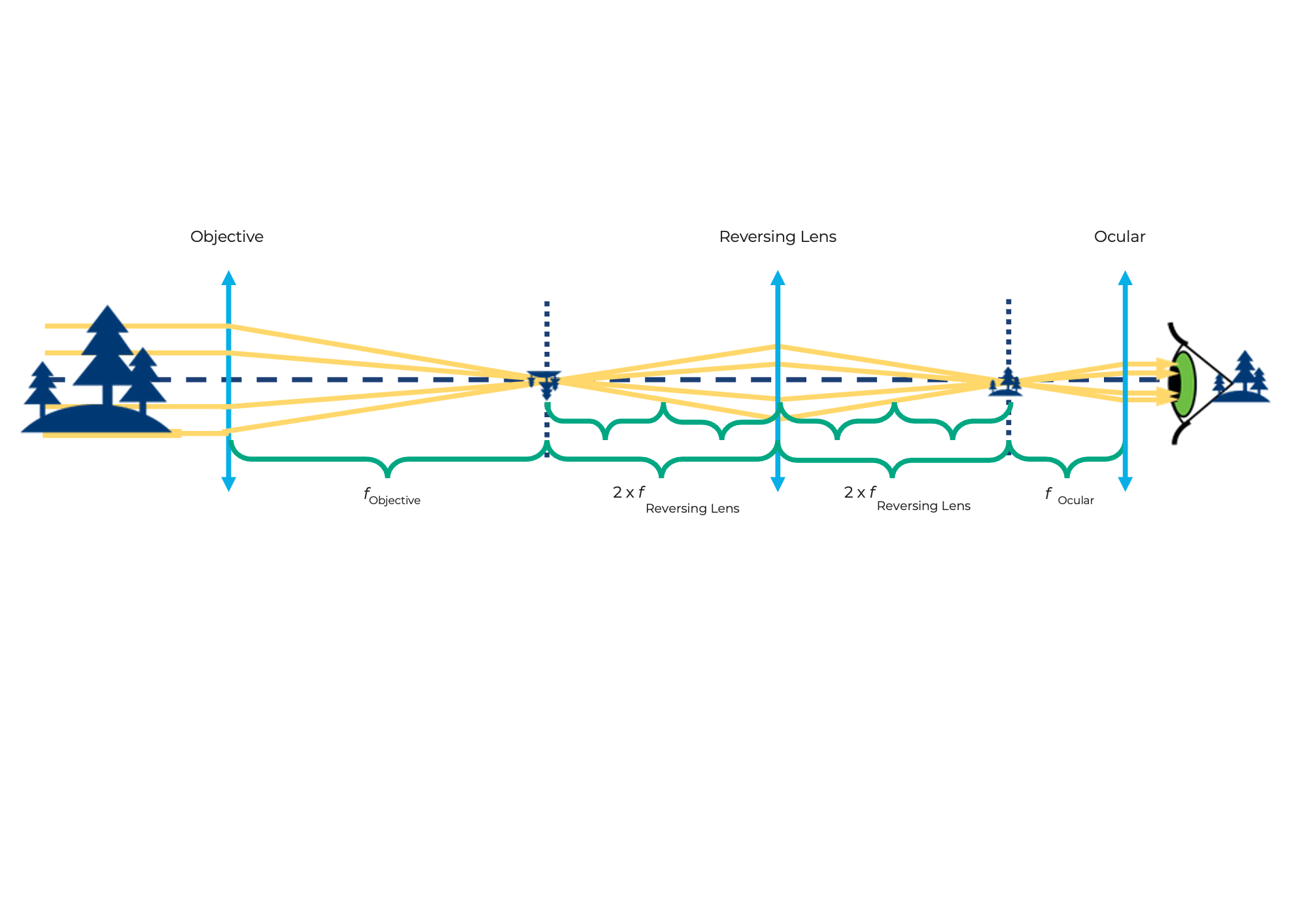
This is how the spotting scope works
The magnification is like that of the Kepler telescope. The erecting lens only changes the orientation (the image is reversed), not the magnification.
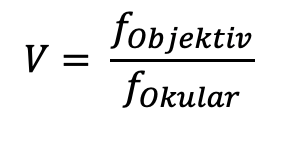
An upright image is necessary for terrestrial observations. True terrestrial telescopes use prism systems to rotate the image and keep it compact.
- Magnified at the same magnification as the Keppler telescope
- Upright
- mirrored